Why Does The Mass Increase In A Chemical Reaction? Exploring The Phenomenon
The Law Of Conservation Of Mass – Todd Ramsey
Keywords searched by users: Why does the mass increase in a chemical reaction why does mass decrease in a chemical reaction, how does a catalyst affect a chemical reaction?, what happens to mass in a chemical reaction, what does it mean for a chemical equation to be balanced?, examples of reactions in which mass changes, is mass a chemical property, equation for when magnesium reacts with oxygen, how does the balanced equation relate to the law of conservation of matter?
What Causes A Change In Mass?
Understanding the factors that lead to a change in mass involves recognizing mass as a form of energy. When an object accelerates and gains speed, it also accumulates additional energy. This energy increment, specifically known as “the increase in mass” (commonly referred to as inertial mass), becomes more noticeable as the object’s velocity increases. Essentially, as an object gains speed, it acquires more energy, which contributes to the observed increase in its mass. This relationship between speed and mass underscores the dynamic nature of mass as it interacts with energy, shedding light on the phenomenon of changing mass in the context of motion.
How Does Mass Affect A Chemical Reaction?
The Law of Conservation of Mass, established by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789, is a fundamental principle in chemistry. It states that the total mass of substances involved in a chemical reaction remains constant; in other words, mass is neither created nor destroyed during the process. This means that the initial mass of any given element before a reaction will be equal to the mass of that element after the reaction has taken place. Understanding this law is crucial in predicting and analyzing chemical reactions, as it provides a foundational framework for quantifying the changes that occur in a system.
Update 9 Why does the mass increase in a chemical reaction
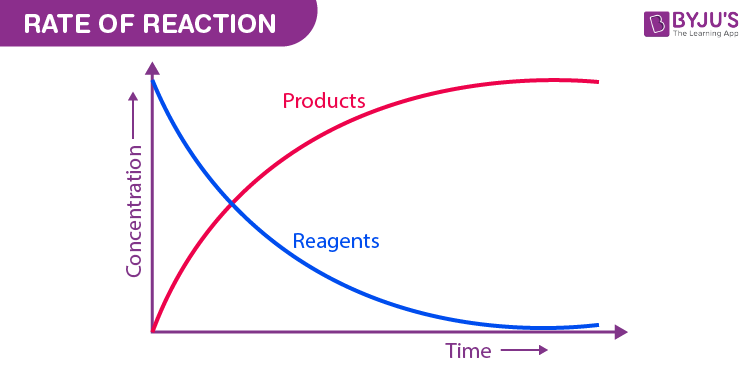



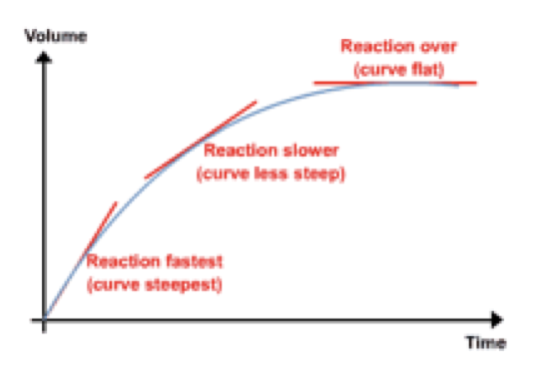

Categories: Aggregate 55 Why Does The Mass Increase In A Chemical Reaction
See more here: future-user.com

Mass does not change during a chemical reaction due to the law of conservation of mass. This law states that the mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products during a chemical reaction in a closed system.So when we think of mass as energy, we can begin to understand why an object will increase its ‘mass’ as it speeds up. As an object increases in speed, so does the amount of energy that it has, this energy is what we refer to as ‘the increase in mass’ (just remember, this is inertial mass).The Law of Conservation of Mass dates from Antoine Lavoisier’s 1789 discovery that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. In other words, the mass of any one element at the beginning of a reaction will equal the mass of that element at the end of the reaction.
Learn more about the topic Why does the mass increase in a chemical reaction.
- Does mass change during a chemical reaction?
- Why Mass Increases with Speed | Futurism
- The Conservation of Mass | Learn Science at Scitable – Nature
- Burning Steel Wool- Does the mass increase or decrease? – YouTube
- Does the Mass of the Reactants Affect the Rate of Chemical …
- Acceleration – CSUN
See more: https://future-user.com/your-money blog
Để lại một bình luận